+90 533 813 89 77
info@bookingforhealth.com
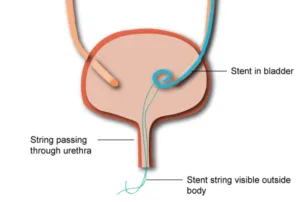
What is the “Ureteral stent” in simple terms
A ureteral stent is like a skinny, bendy straw that doctors put in the tube connecting your kidney to your bladder. It helps keep the tube open so that pee can go from your kidney to your bladder.
Why is a ureteral stent needed?
A ureteral stent may be needed if the ureter is blocked or narrowed due to:
- Kidney stones
- Ureteral strictures (narrowing of the ureter)
- Ureteral tumors
- Ureteral injuries
- Ureteral obstruction caused by other medical conditions, such as cancer or pregnancy
How is a ureteral stent inserted?
A ureteral stent is inserted under cystoscopy, which is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a thin, flexible camera into the urethra and bladder. The stent is then inserted into the ureter using a wire guide.
How long does a ureteral stent stay in?
A ureteral stent can be temporary or permanent. Temporary stents are typically used for a few weeks or months to treat kidney stones or ureteral injuries. Permanent stents are used for people with long-term ureteral obstruction or strictures.
What are the side effects of a ureteral stent?
Ureteral stents can cause some side effects, such as:
- Pain and discomfort
- Urinary frequency and urgency
- Burning urination
- Blood in the urine
- Infection
If you experience any of these side effects, please contact your doctor.
Summary:
Ureteral stents are an effective way to treat a variety of conditions that can block the ureter. However, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of ureteral stenting with your doctor before making a decision.



