+90 533 813 89 77
info@bookingforhealth.com

how long can you live on dialysis
In this artice you will get some information about how long can you live on dialysis
What is Dialysis?
Dialysis stands as a crucial medical procedure, intervening when the kidneys face challenges in optimal functioning.
Hemodialysis involves the blood undergoing a cleansing process through a sophisticated dialyzer, mimicking the role of an artificial kidney. On the other hand, Peritoneal Dialysis utilizes the abdominal membrane to extract waste products and excess fluids.
Acting as both a temporary measure for those awaiting kidney transplantation and a long-term solution for individuals ineligible for transplantation, dialysis offers a personalized approach to renal care.
The frequency and duration of dialysis sessions are tailored to individual needs.
how long can you live on dialysis?
Dialysis is a medical procedure used to remove harmful substances and excess fluids from the body. This machine cleans the patient’s blood and returns healthy blood to the body. However, a crucial aspect is that dialysis is a continuous treatment.
Dialysis treatment can assist individuals in maintaining a healthy life. Nevertheless, this treatment is a constant necessity, and patients need to undergo regular sessions. Failing to receive dialysis can lead to a deterioration in health, underscoring the importance of consistent adherence to this treatment.
While living for an extended period is possible with dialysis, the duration of treatment varies for each patient. Factors such as the individual’s health condition, age, overall well-being, and adherence to the treatment schedule play a role in determining the treatment duration.
It is essential to recognize that dialysis serves as a support for sustaining life, but it does not address all health issues. Therefore, patients must consistently attend their treatment sessions and pay attention to their overall health.
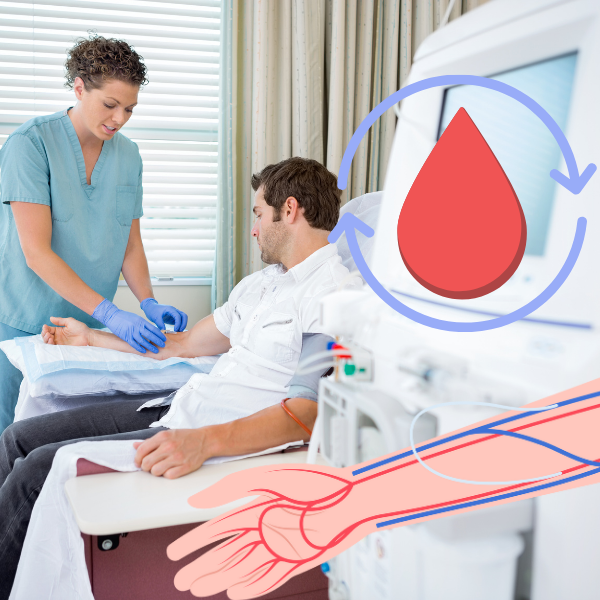
Hemodialysis
Conventional Hemodialysis (HD) is the standard method, where a patient’s blood passes through a machine with a dialyzer to remove waste and excess fluids. Daily Hemodialysis (DHD) is a more frequent version, done five to seven times a week for shorter durations, aiming for enhanced fluid and waste removal.
Peritoneal Dialysis (PD)
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) involves filling the abdomen with dialysis solution via a catheter, allowing waste removal during a dwell time. The used solution is drained, and the process is repeated. Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) uses a cycler to automate exchanges while the patient sleeps, providing flexibility in daily activities compared to CAPD.



