+90 533 813 89 77
info@bookingforhealth.com
Herniated Disc
What is Herniated Disc?
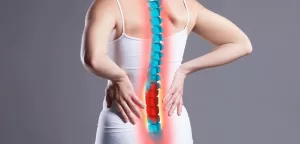
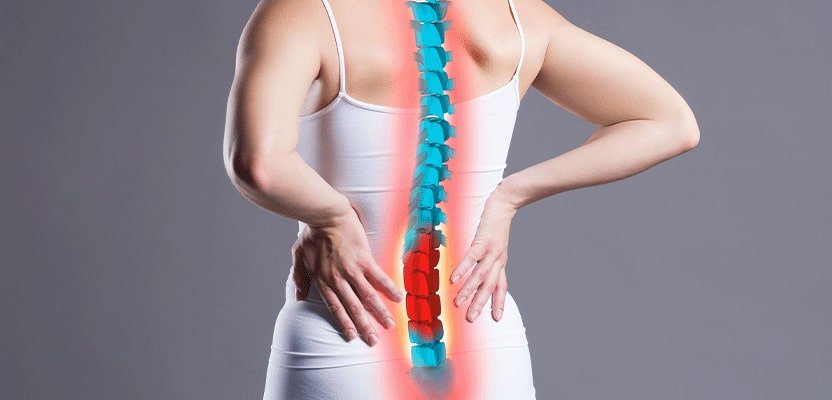
A herniated disc is a condition in which the inner, gel-like material of the spinal disc (nucleus pulposus) bulges out through a tear or crack in the outer layer of the disc (annulus fibrosus). This can occur in any part of the spine but is most common in the lower back (lumbar spine) and neck (cervical spine).
The discs in the spine act as cushions between the vertebrae and absorb shock, but as we age or due to certain physical activities, these discs can become worn and damaged. When this happens, the inner material of the disc may begin to bulge out and press on the nerves or spinal cord, causing pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area.
What Causes Lumbar Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc can occur due to various factors. Some people may be more prone to herniated discs due to genetic reasons. As we age, the discs in our spine can lose their water content and become less flexible, which increases the risk of a herniated disc. In addition, trauma or injury to the spine, such as a car accident or fall, can also cause a herniated disc.
Repetitive movements such as lifting heavy objects or twisting the spine can put pressure on the discs and increase the risk of a herniated disc. Being overweight can put extra strain on the spine and increase the risk of herniated discs. Also, smoking can reduce blood flow to the discs, which can make them more prone to injury.
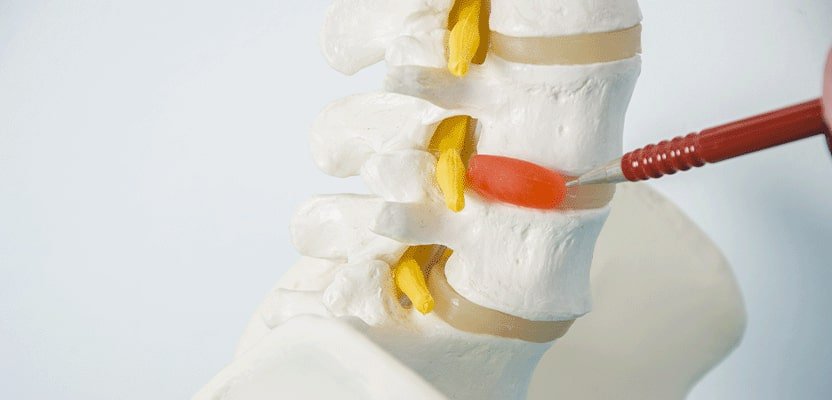
How to Treat Herniated Disc?
The treatment of a herniated disc may vary depending on the individual’s specific condition and the severity of the hernia.
- Conservative Treatment: This includes rest, physical therapy, and medications to alleviate pain and inflammation. Medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and muscle relaxants may be prescribed to reduce pain and muscle spasms.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to alleviate pain, improve the range of motion, and strengthen the muscles that support the spine. Exercises such as core stabilization exercises, McKenzie exercises, yoga, and other appropriate exercises can help to alleviate pain, improve function, and aid in healing.
- Epidural Injections: These injections can help to reduce inflammation and pain by delivering a corticosteroid medication directly to the affected area.
- Surgery: It may be considered in severe cases or if conservative treatment options have been ineffective. Surgery may involve removing a portion of the herniated disc or a procedure known as a discectomy.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic care can help treat herniated discs by providing targeted spinal adjustments, mobilization, and soft tissue therapies, which can reduce inflammation, improve range of motion and reduce pain.
What Should Be Considered After Herniated Disc Treatment?
Several issues should be considered and taken into account after the treatment of herniated disc.
- Follow-up Appointments: It’s important to attend follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider to monitor progress, adjust treatment as needed, and ensure that the individual is on track for a full recovery.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to help improve the range of motion, strength, and function in the affected area.
- Adequate Rest: Adequate rest is important to allow the body to heal, it’s also important to avoid activities that may aggravate the affected area.
- Medications: If medications were prescribed, it’s important to take them as directed and follow up with the healthcare provider to monitor any side effects.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical activity, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can help to prevent future injuries and promote overall health.
- Return to Normal Activities: Gradually returning to normal activities as directed by the healthcare provider, but it’s important to avoid any activities that may aggravate the affected area.
- Avoiding Heavy Lifting: Avoiding heavy lifting is important to avoid any further injury or aggravation of the affected area.
- Continuing Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to prevent future injuries, improve function, and promote overall health.
It’s important to work closely with the healthcare provider to develop an individualized recovery plan and to monitor progress throughout the healing process.